The adoption of LLMs in business is skyrocketing. However, industry analysis suggests most deployments fail to reach production. The critical differentiator is a structured operational framework: LLMOps
What is LLMOps? Beyond Traditional MLOps
LLMOps is a specialized set of practices for managing the entire lifecycle of large language models, focusing on the unique challenges of generative AI in production environments..
While derived from MLOps, LLMOps addresses a different reality. It manages non-deterministic systems where “correctness” is subjective and costs are tied to unpredictable token usage.
Core Differences: LLMOps vs. MLOps
| Aspect | Traditional MLOps | LLMOps (for Generative AI) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Model training, batch inference. | Prompt management, context window optimization, cost per request, hallucination detection. |
| Cost Structure | High upfront training costs. | High, variable inference costs (token-metered). |
| Key Artifacts | Model weights, feature stores. | Prompt templates, RAG indices, guardrail configurations. |
| Evaluation | Accuracy, F1-score. | Multi-dimensional quality (relevance, factuality), human preference ratings. |
| System Nature | A single deployed model. | A compound AI system—orchestration of multiple models and tools. |
The LLMOps Lifecycle: A 4-Stage Framework
Managing LLMs requires a continuous, structured approach. The LLMOps lifecycle revolves around four interconnected stages.
+---------------------+
| 1. Data Exploration |
| & Preparation |
+----------+----------+
|
v
+----------+----------+
| 2. Model Selection |
| & Customization |
+----------+----------+
|
v
+----------+----------+
| 3. Production |
| Deployment |
+----------+----------+
|
v
+----------+----------+
| 4. Continuous |
| Monitoring & Eval |
+----------+----------+
|
+---------> (Feedback Loop to Stage 2)1. Exploratory Data Analysis & Preparation
This foundational stage focuses on curating high-quality data essential for customizing LLMs, directly impacting output accuracy and safety.
Effective LLMOps begins with rigorous data management. A key practice is treating datasets like code—implementing semantic versioning and change logs to ensure reproducibility.
2. Model Selection & Customization
This phase involves choosing the right foundation model and strategically adapting it to your domain, balancing performance with cost.
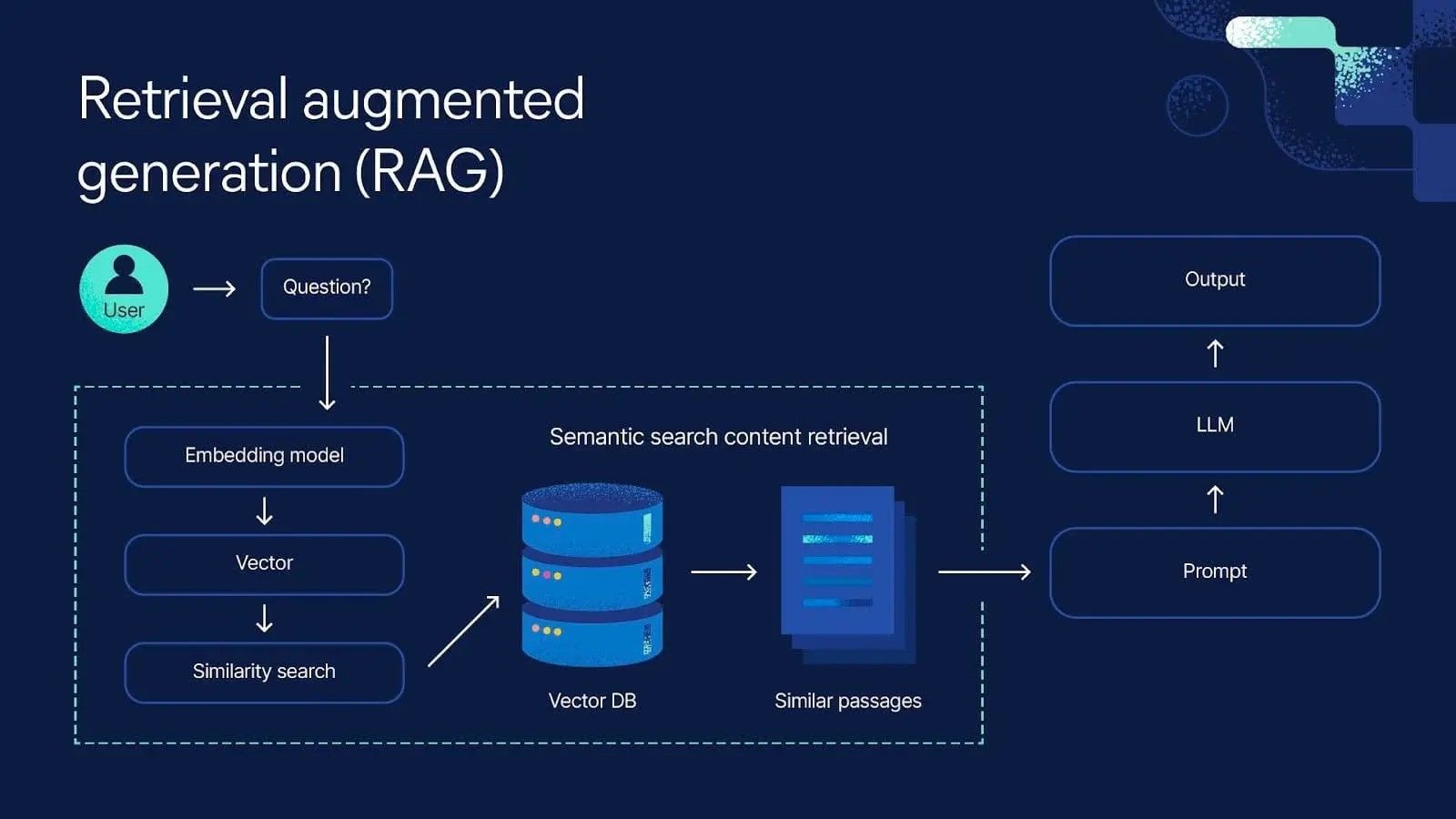
Customization tailors the chosen model through prompt engineering, fine-tuning, or Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG).
# Example: Simple prompt versioning config (YAML)
prompt_template_v1:
system: "You are a helpful assistant for a banking company."
user: "Answer the customer's question: {query}"
prompt_template_v2:
system: "You are a precise banking assistant. Use the provided context."
user: "Context: {context}\n\nQuestion: {query}\nAnswer:"3. Production Deployment Architecture
Moving to production requires infrastructure built for scale, resilience, and cost control.
A robust architecture must include intelligent routing, semantic caching, and guardrails. Semantic caching alone can reduce API calls by up to ~70% for repeated queries.
4. Continuous Monitoring & Evaluation
LLM performance can degrade silently. Continuous monitoring is the critical early-warning system.
Monitoring must track performance metrics (latency, cost per request), quality metrics (hallucination rates), and security (prompt injection attacks).
# Pseudo-code for a basic monitoring check
def log_llm_interaction(prompt, response, model_used):
# Track cost
tokens_used = estimate_token_count(prompt, response)
cost = calculate_cost(tokens_used, model_used)
# Log for analytics
log_to_monitoring_system({
'timestamp': time.now(),
'model': model_used,
'tokens': tokens_used,
'cost': cost,
'prompt_length': len(prompt)
})Critical Challenges & Optimization Strategies
1. Controlling Explosive Costs
LLM inference costs can spiral. Key optimization techniques include:
- Model Quantization: Reducing the precision of model weights to shrink size and speed up inference.
- Prompt Compression: Using specialized techniques to compress prompts, directly reducing token consumption.
- Efficient Scaling: Implementing auto-scaling based on token-based budgets.
2. Ensuring Quality & Managing Hallucinations
The non-deterministic nature of LLMs makes quality assurance unique.
- Implement Compound Evaluation: Combine automated checks, LLM-as-a-judge evaluations, and human feedback.
- Build a Golden Dataset: Maintain a version-controlled set of test cases for continuous regression testing.
Building Your LLMOps Stack
The tooling ecosystem is maturing rapidly.
- Experiment Tracking: MLflow, Weights & Biases.
- Development & Orchestration: LangChain, LlamaIndex.
- Vector Databases: Pinecone, Weaviate.
- Monitoring: LangSmith, Helicone.