Large Language Models (LLMs) are revolutionizing industries, but their tendency to generate confident falsehoods—known as hallucinations—poses a major risk. Over 60% of enterprise AI adopters cite accuracy and trust as top barriers. RAG directly addresses this by creating a bridge between an LLM’s generative power and dynamic, factual knowledge bases, ensuring every response is evidence-based.
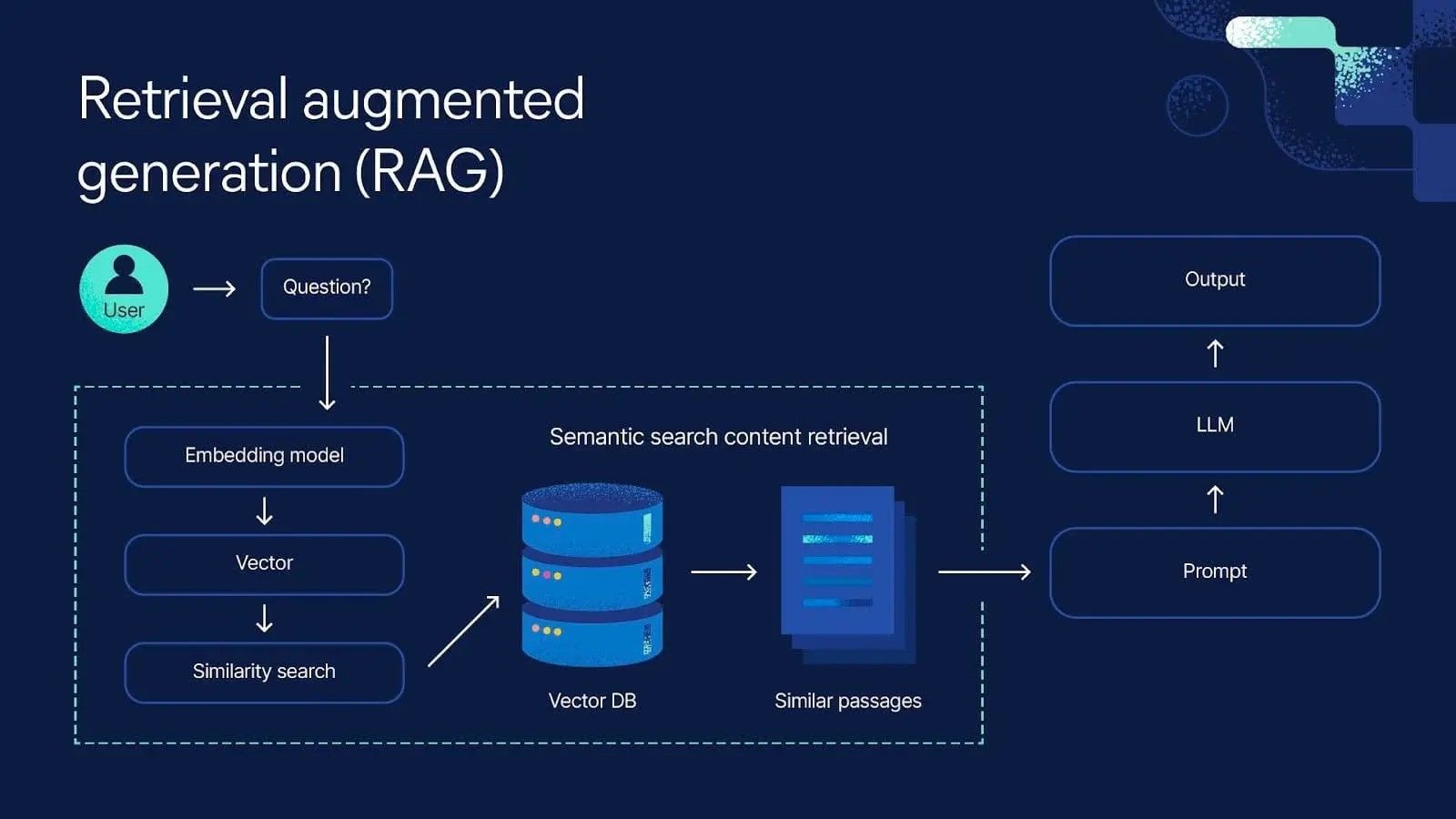
How RAG Works: The Retrieve-Then-Generate Engine
RAG operates through a precise two-phase pipeline that retrieves relevant information before generating a response, ensuring output is grounded in source material.
The core RAG workflow is an elegant, sequential process where retrieval informs generation. This architecture is the key to moving from creative but unreliable chatbots to trustworthy, production-grade AI assistants.
[ User Query ]
|
v
+---------------------+
| 1. Query Embedding |<----(Embedding Model)
| & Retrieval |
+---------------------+
|
v
[Top-K Relevant
Documents]
|
v
+---------------------+
| 2. Prompt |
| Augmentation |
+---------------------+
|
v
+---------------------+
| 3. LLM Generation |---->(GPT-4, Claude,
| with Context | Llama, etc.)
+---------------------+
|
v
[Grounded, Cited
Response]The Four Pillars of a Robust RAG System
- Embedding Model: Converts text into numerical vectors for semantic search.
- Vector Database: Stores and enables lightning-fast similarity searches across millions of document embeddings.
- Retriever: Executes the search strategy to find the most relevant context.
- Generator (LLM): Synthesizes the retrieved context into a coherent, final answer.
Choosing Your Vector Store
| Vector Store | Primary Strength | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Pinecone | Fully Managed Service | Production systems needing scale & reliability |
| Weaviate | Hybrid Search (Vector + Keyword) | Complex queries requiring keyword filters |
| FAISS (Meta) | Maximum CPU/GPU Performance | Research & cost-sensitive, self-hosted solutions |
| Chroma | Developer Experience & Simplicity | Rapid prototyping and local development |
Retrieval Strategies: Beyond Basic Search
- Hybrid Search: Combines dense vector similarity (for meaning) with sparse keyword matching (for exact terms).
- Re-Ranking: Uses a secondary, more powerful model to re-order initial results for higher precision.
- Query Expansion: Rewrites or enriches the user’s query to improve retrieval recall.
Example: Core Embedding and Search Code
# Minimal embedding generation with sentence-transformers
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
doc_embeddings = model.encode(["Your document text here."])
# Essential semantic search logic
query_embedding = model.encode(["User question"])
similarity_scores = np.dot(query_embedding, doc_embeddings.T)
most_relevant_idx = np.argmax(similarity_scores)Overcoming Critical RAG Challenges
Deploying RAG in production requires solving key challenges around retrieval quality, speed, and knowledge freshness to ensure system reliability.
1. Challenge: Poor Retrieval Quality
- Problem: Irrelevant documents poison the context, leading to worse answers.
- Solution: Implement a multi-stage retrieval pipeline (e.g., fast broad search → accurate re-ranking) and use metadata filtering (by date, source, etc.).
2. Challenge: Persistent Hallucinations
- Problem: The LLM ignores good context and invents details.
- Solution: Enforce citation formatting in the prompt and lower the LLM’s
temperatureparameter to reduce creativity.
Example: Hallucination-Reducing Prompt Template
prompt_template = """Answer using ONLY the context below. Cite sources [1], [2]... Context: {retrieved_text} Question: {user_query} Answer:"""3. Challenge: High Latency
- Problem: The added retrieval step slows down responses.
- Solution: Implement semantic caching (store answers to similar past queries) and use Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search in your vector database for speed.
4. Challenge: Stale Knowledge
- Problem: The knowledge base becomes outdated.
- Solution: Establish an automated pipeline for incremental updates, versioning new documents as they arrive.
Advanced RAG Patterns for Complex Tasks
Sophisticated RAG techniques like query decomposition and adaptive retrieval tackle complex questions and optimize cost-performance trade-offs.
- Query Decomposition (Step-Back Prompting): Breaks a complex query into simpler sub-questions, retrieves answers for each, and synthesizes a final response. Ideal for comparative or multi-faceted questions.
- Hypothetical Document Embeddings (HyDE): Instructs the LLM to generate a hypothetical ideal answer first, then uses that to find the most semantically similar real documents. Boosts retrieval relevance for abstract queries.
- Self-RAG: An advanced pattern where the LLM itself learns to decide when to retrieve, optimizing for cost and speed on queries it can answer from its own parametric knowledge.
The RAG Implementation Checklist
- Define Scope: Choose a specific, high-value use case (e.g., internal docs Q&A).
- Prepare Knowledge Base: Clean, chunk, and embed your source documents.
- Select Stack: Choose embedding model (e.g.,
text-embedding-3-small) and vector DB. - Build Pipeline: Implement retrieval, context augmentation, and generation.
- Optimize Retrieval: Test hybrid search and re-ranking strategies.
- Engineer Prompts: Create instructions that mandate source citation.
- Implement Evaluation: Track Retrieval Hit Rate and Answer Faithfulness.
- Plan for Updates: Design a process to refresh the knowledge base.
Conclusion: The Path to Trustworthy AI
RAG is not just an architectural choice; it’s a foundational shift towards transparent, updatable, and trustworthy AI. By tethering generative models to dynamic knowledge, it transforms LLMs from oracles of uncertain accuracy into precise reasoning engines. The future lies in multi-modal RAG (understanding images, tables, and code) and active retrieval systems that intelligently seek information. For any enterprise deploying AI, mastering RAG is the essential step from promising prototype to reliable, scalable production system.